Smile Design & Aesthetic Dentistry
Smile Design: Personalized Approach in Aesthetic Dentistry
Smiling is the most important part of a person’s facial expression. In our era, where aesthetic perception has come to the forefront, individuals increasingly pay attention to their appearance, which has brought new approaches to dentistry. Smile design, as one of the most advanced fields of aesthetic dentistry, aims to create a patient-specific, aesthetic, and functional smile by evaluating the harmony of teeth, gums, lips, and facial structure.
What is Smile Design?
Smile design is a personalized aesthetic and functional dental treatment planning considering many factors such as the individual’s facial shape, gender, age, lip structure, tooth alignment, gum level, and skin tone. This process combines digital technologies, aesthetic criteria, and multidisciplinary treatment approaches.
The history of aesthetic dentistry gained momentum in the 1980s with the development of porcelain veneers and teeth whitening procedures. However, the concept of “smile design” emerged in the 1990s by integrating these applications into a holistic approach. Since the 2000s, digital analysis and planning methods like Digital Smile Design (DSD) have taken this concept to a more advanced level.
Basic Components of an Aesthetic Smile
Smile design is not only teeth whitening or reshaping. To achieve an aesthetic smile, the following elements are evaluated together:
1. Teeth
Shape, size, color, and alignment of teeth
Tooth gaps, crowding, and wear
Symmetry of front teeth and incisal edge line
2. Gums (Gingiva)
Gum level and symmetry
Gummy smile (excessive gum visibility)
Gum color changes or inflammation
3. Lips and Face
Lip movements and smile line
Amount of teeth visible during smiling
Face shape and lip thickness
4. Golden Ratio and Aesthetic Rules
Proportion of teeth to face
Midline harmony
Proportions among teeth (e.g., 1.618 golden ratio)
Techniques Used in Smile Design
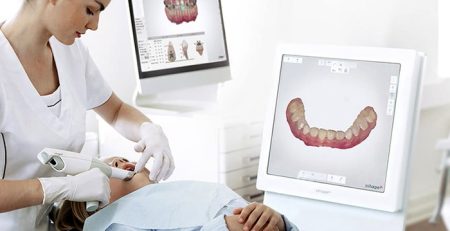
1. Digital Smile Design (DSD) DSD allows the digital design of the ideal smile using the patient’s photos and videos. The patient can see the final result before treatment starts.
2. Mock-up and Wax-up Applications
Wax-up: Trial restorations made on models.
Mock-up: Temporary trial of this design in the patient’s mouth.
3. Aesthetic Dentistry Applications
Porcelain Veneers: Thin ceramic layers bonded to the front surface of teeth.
Zirconium Crowns: Durable and natural-looking full crowns.
Composite Bonding: Minor corrections made with tooth-colored materials.
Teeth Whitening: Applied to lighten tooth color.
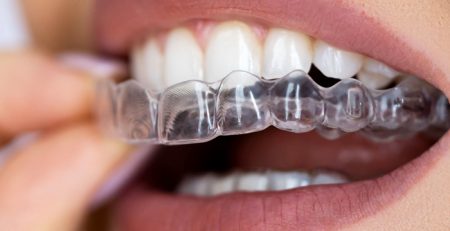
Orthodontic Treatment or Clear Aligners: Used to correct tooth alignment.
Gum Aesthetics: Includes procedures like gingivectomy and laser contouring.
Stages of Smile Design
Examination and Determination of Patient Expectations
Photography and video recordings
Learning aesthetic and functional expectations
Digital Analysis and Planning
Digital planning with DSD
Calculations of tooth, lip, and face proportions
Mock-up Application
Testing the planned smile in the mouth
Making necessary adjustments
Treatment Process
Orthodontic, periodontal treatment, and aesthetic restorations are applied
Result and Follow-up
Final restorations are applied
Evaluation with photos and videos
Periodic follow-ups
Multidisciplinary Approach
Smile design requires collaboration among many dental specialties, not just one:
Aesthetic dentistry
Orthodontics
Periodontology
Prosthetic dentistry
Oral surgery
Cooperation among these disciplines ensures long-lasting and healthy aesthetic results.
Advantages
– Personalized planning
Aesthetic and functional improvement
Increased patient confidence
Ability to see results before treatment (DSD and mock-up)
High patient satisfaction
Who is it Suitable For?
– Individuals with aesthetic concerns
Those with issues in tooth shape, color, or alignment
People dissatisfied with previous restorations
Individuals unhappy with their smile and seeking change
Who is it Not Suitable For?
– Those with serious systemic diseases
People with poor gum health (treatment needed first)
Individuals with insufficient oral hygiene
Smile design is an art and science that combines aesthetic expectations with scientific criteria. Planned according to the person’s facial structure, expressions, and personal wishes, this application positively affects not only appearance but also speech, chewing, and confidence. With the advancement of digital technologies, smile design now offers more predictable, faster, and successful results. However, it should be remembered that every individual is unique, and a natural result cannot be achieved without a plan suited to this uniqueness.