What Causes Tooth Decay in Children? Symptoms, Early Diagnosis and Treatment
What causes tooth decay in children? Learn about symptoms, early diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive methods for cavities from Melsadent pediatric dentistry experts.
What causes tooth decay in children? Learn about symptoms, early diagnosis, treatment methods, and ways to prevent cavities from Melsadent experts.
Tooth decay in children is one of the most common chronic childhood diseases worldwide. Cavities that start at an early age do not only create aesthetic problems; they can also negatively affect children’s chewing, speech, sleep patterns, and overall health. Moreover, cavities in primary (baby) teeth directly impact the health of permanent teeth in later years, making early intervention extremely important.
As Melsadent Oral and Dental Health Polyclinic, we explain in detail the causes of tooth decay in children, its symptoms, the importance of early diagnosis, and modern treatment methods.
What Causes Tooth Decay in Children?
Many factors play a role in the development of tooth decay in children:
1. Poor Oral and Dental Hygiene
Children often develop regular toothbrushing habits late. As plaque accumulation increases, the risk of cavities rises.
2. Sugary and Sticky Foods
Foods such as chocolate, candy, gummies, cakes, cookies, and fruit juices stick to the tooth surface and create an ideal environment for bacteria to multiply.
3. Nighttime Bottle Feeding (Baby Bottle Tooth Decay)
Children who consume milk, fruit juice, or sugary drinks from a bottle throughout the night experience faster cavity formation. This is because saliva flow decreases during sleep, creating an ideal environment for bacteria.
4. Genetic Predisposition
In some children, the structure of the tooth enamel may be weaker, making cavities more likely to develop.
5. Insufficient Water Intake
Water containing fluoride strengthens tooth enamel. Children who drink less water have a higher risk of cavities.
6. Frequent Snacking
Frequent snacking during the day causes teeth to be constantly exposed to acid, increasing the risk of tooth decay.
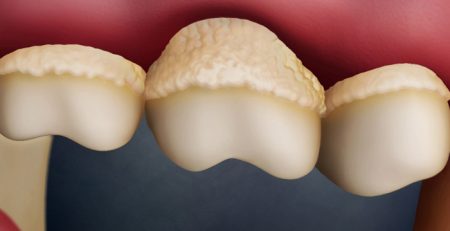
Symptoms of Tooth Decay in Children
In early stages, cavities in children may not cause noticeable symptoms. Therefore, when cavities are detected, they are often already advanced. Symptoms to watch for include:
– White or yellow spots on teeth
– Sensitivity to hot and cold
– Pain while eating
– Brown or black spots between teeth
– Bad breath
– Avoidance of using a specific tooth
– Toothache that wakes the child up at night
When these symptoms are observed, it is essential to consult a pediatric dentist (pedodontist) without delay.
Why Is Early Diagnosis Important?
Early diagnosis allows tooth decay in children to be controlled before it progresses. Detecting cavities at an early stage offers the following advantages:
– Easier treatment with smaller fillings
– Reduced risk of tooth loss
– Prevention of pain for the child
– No negative impact on jaw development
– Faster and more cost-effective treatment process
– As Melsadent experts, we recommend dental check-ups for children every 6 months.
Treatment of Tooth Decay in Children
Various treatment methods are applied depending on the child’s age, the size of the cavity, and the condition of the tooth.
1. Fluoride Application
It strengthens tooth enamel and can stop early-stage cavities from progressing. It is especially effective during the white spot stage.
2. Fissure Sealant (Sealing of Tooth Grooves)
Since the grooves of molar teeth are highly prone to bacterial accumulation, protective fissure sealants significantly reduce the risk of cavities.
3. Filling Treatment
Applied in moderately advanced cavities. Aesthetic white (composite) fillings are preferred, restoring the tooth to its original form after decay removal.
4. Root Canal Treatment (Primary Tooth Root Canal)
If decay has reached the nerve tissue, root canal treatment can also be performed on primary teeth. Preserving baby teeth is crucial, as early tooth loss can disrupt jaw development and tooth alignment.
5. Pediatric Crown (Primary Tooth Crown)
Durable metal or zirconia crowns stop the progression of decay and are especially effective for severely damaged primary teeth.
6. Tooth Extraction
If the cavity is too advanced and cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary. In such cases, a space maintainer may be required.
Ways to Prevent Tooth Decay in Children
Preventing cavities in children is much easier and more important than treatment. Key preventive steps include:
Developing a Toothbrushing Habit
– Ages 0–3: With parental assistance
– Ages 3–6: Under supervision with a soft-bristled toothbrush
– Age 6 and above: Regular brushing twice a day
Proper Nutrition Management
– Sugary snacks should be limited
– Nighttime bottle feeding should be stopped
– Acidic drinks should be strictly avoided
Regular Dental Check-Ups
A pedodontist examination every 6 months is of great importance.
Fluoride Support and Preventive Treatments
Professional fluoride applications and fissure sealant procedures significantly reduce cavity risk.
Parental Education
A child’s oral health is largely shaped by parental awareness. Therefore, educating families is essential.
Pediatric Dentistry Services for Children at Melsadent
Melsadent has a pediatric dentistry (pedodontics) department specially designed to provide children with fear-free and comfortable dental treatments.
Privileges offered for pediatric patients at Melsadent
– Child-friendly, sterile, and safe clinical environment
– Experienced pediatric dentistry specialists
– Digital X-rays and modern treatment methods
– Painless and fast procedures
– Preventive treatments specifically for children
– Family education and consultation support
The right way to protect your child’s oral health is professional support from a pediatric dentist.